Land has potential that is enormous in the real estate. One of the most important of the technical parameters which stipulate the extent to which that potential can be legally exploited is the Floor Space Index, or the FSI. The meaning of Floor Space Index is also critical when it comes to developers, investors and buyers who go to purchase a property but want to utilise fully the land without contravening the rules of urban development.
This blog defines the definition of a Floor Space Index, how it is calculated, the significance of the index and its connection with FAR (Floor Area Ratio) – so that you understand why it has become so crucial in the current real estate.
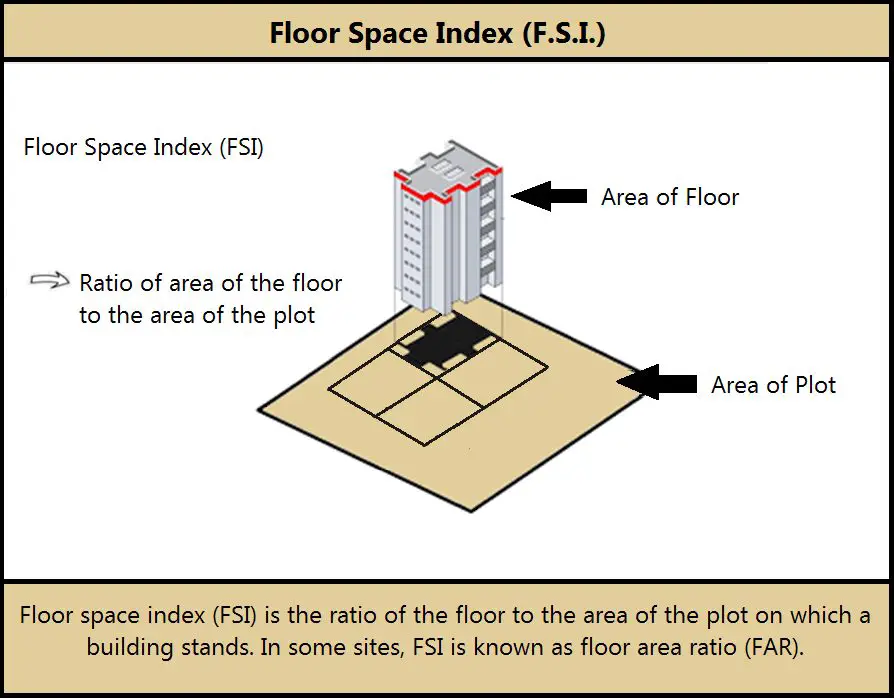
Floor Space Index in Real Estate?
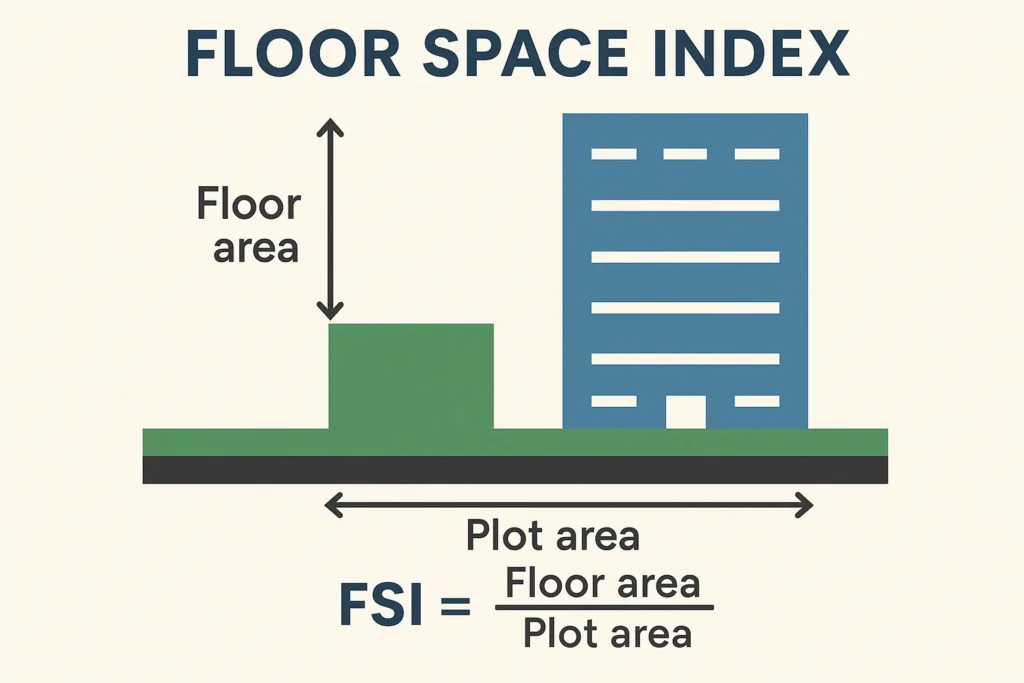
The Full Space Index of Floor Space Index (FSI) is a ratio, which stipulates the allowable area that can be built on a particular piece of land. Simply put’ it informs you of the amount of construction you can execute depending on the size of the plot.
The definition of Floor Space Index is:
FSI = built-up area (the total of all the floor areas)/plot area.
Floor Space Index real estate norms are applied as a means for municipal authorities to regulate building density and provide safety and sustainable development. As an illustration, tall buildings in the city could be built with high FSI, whereas low FSI guarantees the provision of more open spaces in suburban regions.
Why You Need to Know About Floor Space Index
Knowledge of what the Floor Space Index is of paramount importance to everyone dealing with real estate since it has a direct bearing on the following:
- The height and size of the buildings that can be built.
- The price of land and property, as in many cases, higher FSI translates to greater returns.
- Legal regulations, as breaking the FSI may lead to fines or demolition.
It can be that you are a developer and you are planning a big project, or you are a buyer and you are going to buy an apartment; knowing the Floor Space Index formula and the maximum limits that you can go to will help you to make sound, profitable, and legal decisions.
Floor Space Index Formula Explained
Understanding the Floor Space Index formula is essential for all real estate stakeholders. It determines how much construction is legally allowed on a plot.
| Parameter | Description | Formula / Example |
|---|---|---|
| Formula | FSI = Total Built-up Area / Total Plot Area | |
| If expressed in % | FSI (%) = (Total Built-up Area ÷ Total Plot Area) × 100 | |
| Example | Plot Area = 1,000 sq. m. Built-up Area = 2,000 sq. m. | FSI = 2.0 or 200% |
| Meaning | You can construct up to 2,000 sq. m. total built-up area on a 1,000 sq. m. plot | FSI defines total permissible construction |
Example:
Assuming that you have 1,000 sq. m. of land and your Floor Space Index is 2.0 (or 200%), then the maximum built-up area is 2,000 sq. m.
It implies that you can construct either 2 floors of 1,000 sq. m. or any arrangement that comes to 2,000 sq. m.
The awareness of the formula of the Floor Space Index assists designers and constructors to use the ground efficiently and create effective yet compliant buildings.
Difference Between FSI and FAR
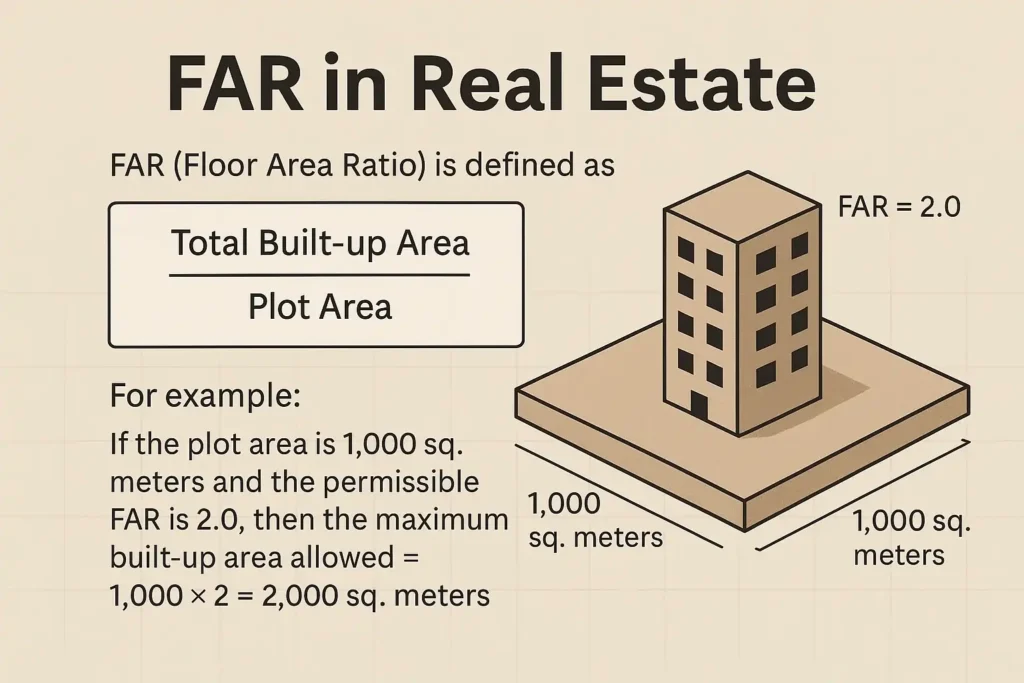
FSI and FAR (Floor Area Ratio) are often used interchangeably, but they differ in representation. Both measure the ratio of built-up area to land area, but the units vary.
| Aspect | Floor Space Index (FSI) | Floor Area Ratio (FAR) |
|---|---|---|
| Expression Format | Percentage (e.g., 200%) | Decimal Ratio (e.g., 2.0) |
| Formula | (Built-up Area ÷ Plot Area) × 100 | Built-up Area ÷ Plot Area |
| Example | 200% | 2.0 |
| Usage | Common in India & Asia | Common in Western countries |
| Concept | Both mean the same – total permissible construction | Identical concept, different representation |
In short, FSI = FAR × 100.
If FAR = 2.0, FSI = 200%.
Thus, the Floor Space Index definition and FAR definition are identical, only expressed differently.
Factors Affecting Floor Space Index
There is no fixed value of what the Floor Space Index is in real estate; it varies based on a number of factors that are specified by the municipal or state authorities:
Location and zoning Urban centres tend to have better FSI to permit vertical growth, whereas suburbs are less restrictive.
- Construction Type: A commercial building project (as compared to a residential building project) tends to have a greater FSI because of the infrastructure requirement.
- Road Width: Adjoining roads that are wider in nature can support a larger FSI, and thus denser development can occur.
- Infrastructure Availability: Locations that have high water availability, drainage, and power tend to get increased FSI.
- Government Incentives: The developers are allowed to buy premium FSI at times to develop beyond the ordinary threshold in the redevelopment or affordable housing projects.
These parameters guarantee the balanced development and urban growth.
Significance of Floor Space Index in Real Estate Development.
Key Aspects of Floor Space Index
Here’s a quick table summarising the major factors that influence the Floor Space Index in real estate:
| Factor | Impact on FSI | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Location & Zoning | Higher in metro or urban areas | Allows taller buildings and dense housing |
| Type of Building | Commercial buildings get higher FSI | To support business infrastructure |
| Plot Size | Larger plots may qualify for extra FSI | Encourages planned developments |
| Road Width | Wider roads = higher FSI | Supports increased traffic and density |
| Infrastructure | Strong civic systems allow more FSI | Availability of water, sewage, power |
| Government Policies | Bonus or Premium FSI possible | Available for green or affordable projects |
Each of these aspects determines how much floor space you can construct legally on a given plot.
Importance of Floor Space Index in Real Estate Development
Maximises Land Utilisation: It is how well land can be utilised in building.
- Ensures Urban Balance: Controlled FSI will eliminate congestion and overloaded infrastructure.
- Influences Property Value: An increase in FSI enhances the development prospect and market value.
- Guides Building Design: Architects design layout plans, the number of floors to be constructed and open space design depending on the permissible FSI.
- Enhances Sustainability: FSI is able to ensure sustainability in the environment by regulating the density.
Therefore, the concept of Floor Space Index is crucial to both urban planners and property owners as well.
Advantages of Floor Space Index Regulation
FSI is not a restriction to some, but on the contrary, it is associated with numerous advantages:
- Encourages strategic urbanisation and structured urban development.
- Provides legal and safe construction.
- Developers are those who determine project feasibility and maximise ROI.
- Balances the aesthetic features of a city between open space and developed territory.
- Makes money for civic organisations on high-priced FSI authorisations.
Conclusion
Floor Space Index (FSI) is more than merely a technical term; it is also a basis of smart and sustainable real estate development. FSI ensures the cities develop in an orderly, effective and ecologically friendly manner by specifying the extent of construction that may be done on a piece of land.
No matter whether you are a developer, architect, or homebuyer, understanding the meaning, formula, and definition of the Floor Space Index makes it possible to make informed decisions. FSI is also among the most significant concepts in real estate, as it is a planning tool and a compliance measure, which shapes the cityscape, regulates development, and ensures the balance within the city.
FAQs Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is Floor Space Index in real estate?
The Floor Space Index (FSI) in real estate refers to the ratio between the total built-up area of a building and the total area of the plot. In simple terms, it defines how much construction is allowed on a particular piece of land. Understanding what the Floor Space Index is helps builders and buyers plan projects within legal limits and optimise land use efficiently.
2. What is the Floor Space Index meaning and definition?
The Floor Space Index meaning, or Floor Space Index definition, is a regulatory measure used by municipal authorities to control building density and maintain balanced urban growth. It ensures that construction follows safety, infrastructure, and zoning norms. A higher FSI allows taller or larger buildings, while a lower FSI ensures more open spaces and controlled development.
3. What is the Floor Space Index formula?
The Floor Space Index formula is:
FSI=Total Built-up Area / Total Plot Area
If expressed as a percentage, multiply by 100. For example, if a 1,000 sq. m. plot has a total built-up area of 2,000 sq. m., then FSI = 2.0 or 200%. This formula helps architects and developers plan projects as per building regulations.
4. What is the full form of FSI in real estate?
The full form of FSI is Floor Space Index. It’s also known as the Floor Area Ratio (FAR) in some regions. Both terms describe the same concept but differ in expression — FSI is represented as a percentage (e.g., 200%), while FAR is shown as a ratio (e.g., 2.0).
5. Why is knowing the Floor Space Index important in construction?
Understanding the Floor Space Index is vital because it influences the design, height, cost, and legal compliance of a building. It also affects land valuation, future expansion potential, and project feasibility. Awareness of what Floor Space Index is ensures developers and buyers invest in safe, compliant, and profitable real estate projects.




